//16.3 Youth watch
A Global Insight into Youth Crime,
Paths to Rehabilitation
by Bimal Mirwani
Juvenile delinquency and youth crime have seen notable trends and shifts globally in recent years. Given the complex landscape and multifarious nature of the challenge, attention needs to be given to effective strategic intervention.
Japan
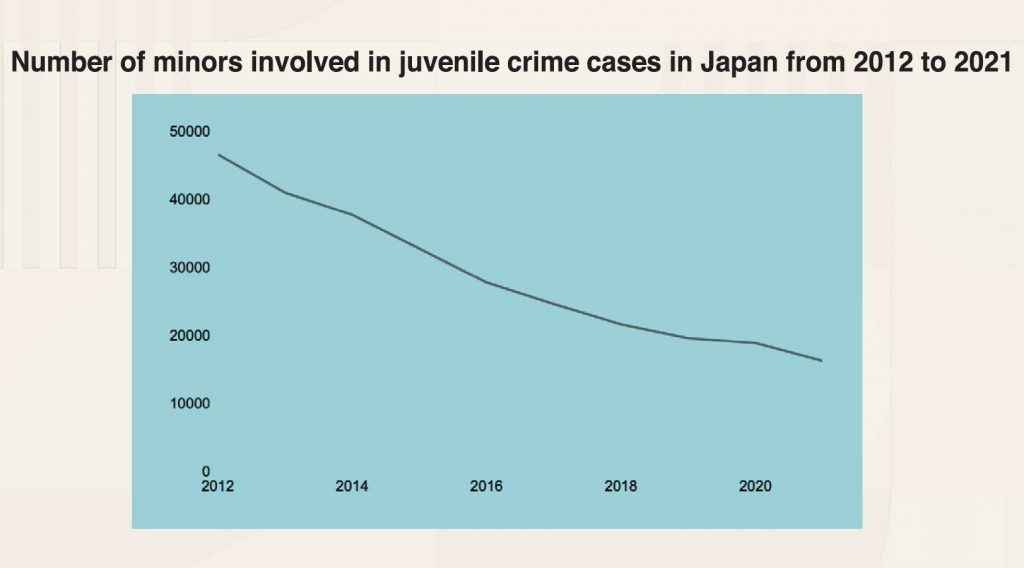
Juvenile crime in Japan has seen a steady downward trend over the past decade, with the number of minors arrested totalling just over 16,000 in 2021, according to data from Statista. This can be attributed to factors including effective rehabilitation programmes and a low unemployment rate. However, a notable shift occurred in 2022, when arrests of 14-20-year-olds saw a 2.5% annual increase from 2021. One prominent reason was physical or psychological violence among family members.
Most common types of crime
- Theft-related activities
- Bodily harm to others
Rehabilitation Programmes
Japan has numerous rehabilitation programmes including Juvenile Training Schools that provide education and vocational training under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Justice. The ministry also collaborates with other governmental bodies to offer employment support for juvenile offenders. Volunteer probation officers and mentorship programmes like the Big Brothers and Sisters Movement (BBS) are also available.
Singapore
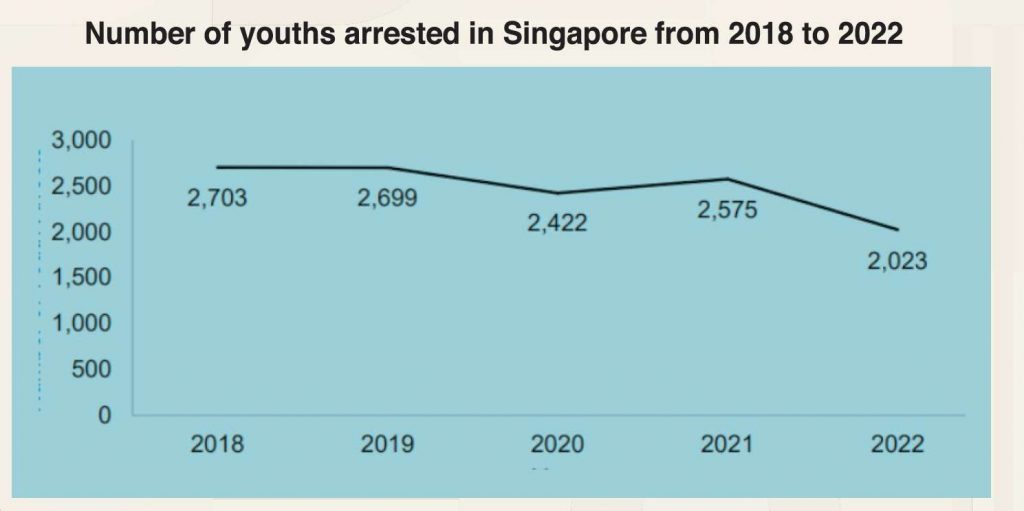
Singapore has seen an overall downward trend in youth crime since 2018, barring a slight increase in 2021. In 2022, the country registered 2,023 juvenile arrests – the lowest in five years. This decline likely stemmed from the COVID-19 pandemic and may have been also influenced by the receptiveness of young individuals to preventive and rehabilitative interventions.
Most common types of crime
- Shop theft
- Cheating and related offences
- Sexual offences
Rehabilitation Programmes
The Guidance Programme (GP) is a notable Singaporean rehabilitation initiative for young offenders. Run by SHINE under the authority of the Ministry of Social and Family Development, the programme offers individual, group, and family counselling sessions focused on emotional management, problem-solving, and building healthy relationships. Successful completion allows participants to avoid formal charges. Care Corner, a non-profit organisation, also offers services to juvenile criminals through casework and group sessions to help them navigate their own challenges.
Australia
From 2022-2023, law enforcement agencies processed 48,014 10-17-year-olds involved in criminal activities. This marked a notable increase of 6%, or 2,804 more offenders than in 2021-2022. The youth offender rate increased from 1,778 to 1,847 per 100,000 persons, the first uptick since 2009-2010.
Most common types of crime
- Acts intended to cause injury
- Theft
- Unlawful entry with intent
Rehabilitation Programmes
The Australian Law Reform Commission states that numerous structured rehabilitation programmes offered by local governments and other organisations cover areas such as education, employment, recreation, independent living skills, drug and alcohol counselling, pastoral care and anger management. Alternatively, young offenders can take part in the Changing Habits and Reaching Targets programme (CHART) programme offered in Queensland and New South Wales. Its primary objective is diminishing the likelihood of recidivism among juveniles.
India
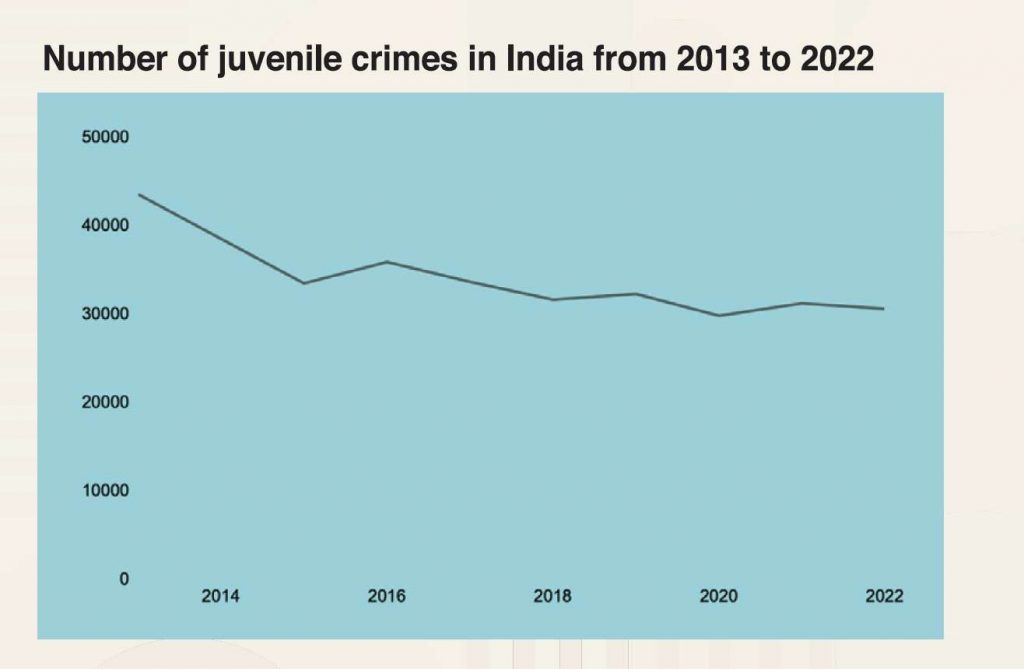
India saw a noticeable dip of approximately 30% in juvenile crime from 2013-2022. According to National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) data, the number plummeted from 43,506 to 30,555.
Most common types of crime
- Thefts
- Robberies
- Causing hurt or grievous hurt
- Rapes and assaults
Rehabilitation Programmes
India’s initiatives to rehabilitate young criminals include Juvenile Justice Boards (JJBs), which are supported by the Integrated Child Protection Scheme (ICPS) of the Ministry of Women and Child Development. A key responsibility of JJBs is overseeing the rehabilitation and reintegration process of juvenile offenders. Observation Homes and Special Homes under the jurisdiction of state governments, guided by the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015, also provide rehabilitation through counselling, education, and vocational training.
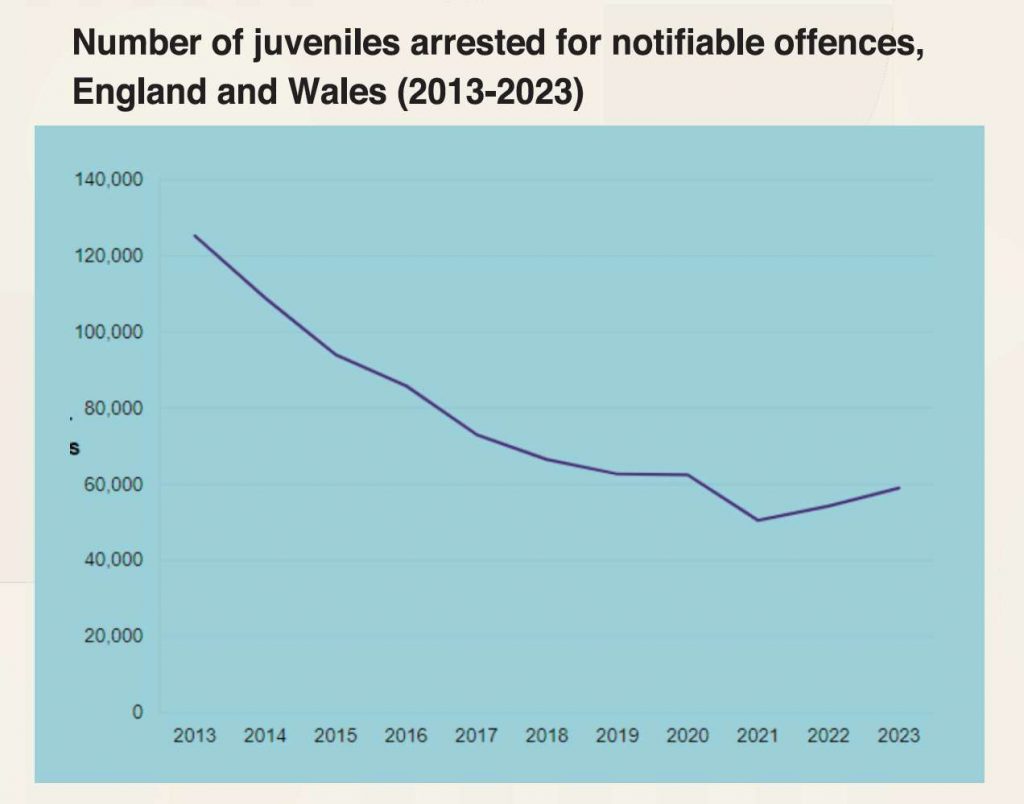
United Kingdom
From April 2022 to March 2023, there were approximately 59,000 arrests of 10-17-year-olds for notifiable offences in England and Wales, representing a 9% increase over the previous year. However, arrests decreased by almost a half compared to the figure in 2013.
Most common types of crime
- Theft and handling stolen goods
- violence against the person
- criminal damage
Rehabilitation Programmes
Youth Offending Teams are central to the rehabilitation of young offenders in England and Wales. They operate at the local council level and assess the risks and needs of young people, creating tailored plans to address these factors. This may involve face-to-face meetings, group work or other community-based interventions. Also at a local level, various programmes offer vocational training and support services, such as counselling, mentoring, and educational assistance. Additionally, Novus, a leading provider of education in prisons, plays a significant role in rehabilitating young offenders through its educational initiatives.
United States
The US had a high number of juvenile criminals in 2020, with 424,300 arrests made. However, the figure represents a drastic 71% drop compared to 2011. Many factors played a hand in this decrease, including raised attention to at-risk youth and a notable shift from punishment to rehabilitation.
Most common types of crime
- Simple assault
- Larceny-theft
- Drug abuse violations
Rehabilitation Programmes
The Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention operates the Youth Reentry Program, which aims to help minors successfully reintegrate into society through mentoring and family engagement. Furthermore, many juvenile facilities across the country offer educational programmes and job training to provide young offenders with the necessary skills for employment and further education.
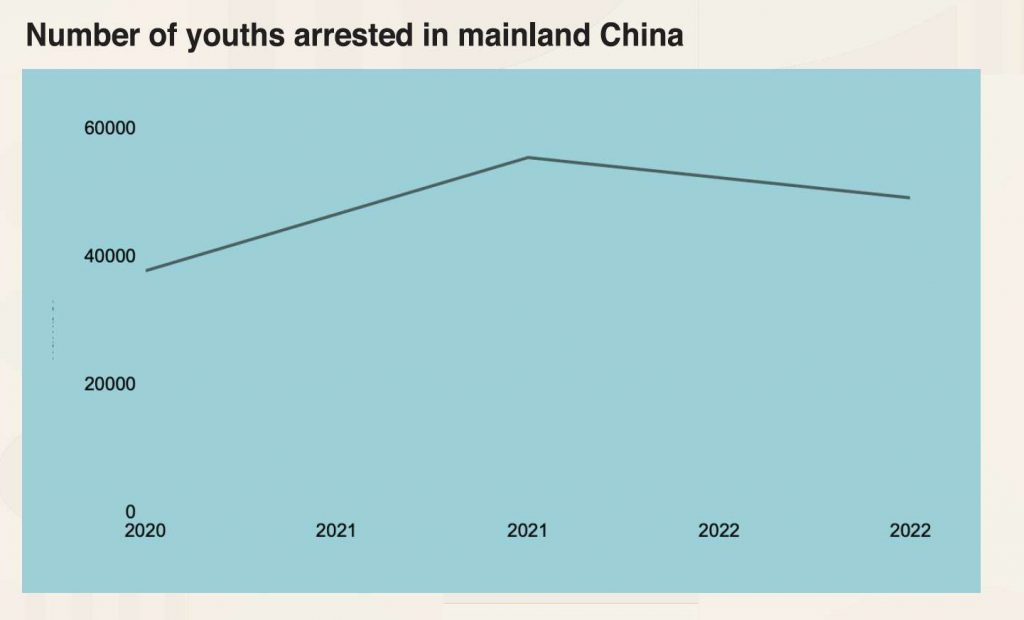
Mainland China
Mainland China recorded a concerning rise in juvenile delinquency, following a steady decrease since 2014, according to the Supreme People’s Procuratorate, the highest procuratorial organ of the People’s Republic of China.
The overall number of minors suspected of crimes has risen, with 61,295 minors reviewed for prosecution in 2022, marking a 5.12% increase from the previous year. Additionally, there is a notable uptick in the involvement of younger offenders, particularly those aged 14 to 16, whose proportion in the overall juvenile crime statistics has increased.
Most common types of crime
- Theft
- Gathering to fight
- Rape
Rehabilitation Programmes
Mainland China’s legislation for juvenile offenders includes the revised Law on Prevention of Juvenile Delinquency. It mandates that children who misbehave should be educated and rehabilitated in special correctional schools, with decisions made collaboratively by education and public security departments. The aim is to prevent recidivism by addressing the root causes of delinquency, such as family dynamics and the offender’s school environment. Young criminals may be placed in reformatories or work-study schools, where the focus is on education, vocational training, and behavioural correction. These institutions target 13-28-year-olds who have committed minor offences or are first-time offenders.
Hong Kong
Hong Kong saw mixed figures for juvenile crime in the first half of 2024, according to the Hong Kong Police Force, with offenders aged 10-15 falling from 591 in the same period in 2023, to 536. This represented a 9.3% decrease. While among 16-20-year-olds, arrests rose from 938 to 1,005 in the same period, logging a 7.1% increase.
Deception offences have seen a significant increase among young offenders, with 217 arrests in the first half of 2023, more than double the 115 arrests in the same period last year.
Most common types of crime
- Wounding and serious assault
- Deception
- Miscellaneous theft
Rehabilitation Programmes
Hong Kong has a plethora of rehabilitation programmes for young offenders, including the Change Lab and Youth Lab, both of which were established in 2022 and are run by the Correctional Services Department (CSD). The Change Lab allows young offenders under supervision to rebuild a law-abiding life, while the Youth Lab is a specialised treatment unit at Pik Uk Correctional Institution that provides psychological programmes to cultivate “pro-social values.” Notably, programmes provide guidance and support to young offenders so that they can reintegrate into society with a lower chance of recidivism.
Promising Solutions for Pressing Problems
Juvenile delinquency, youth crime and rehabilitation demand a comprehensive and nuanced approach that addresses underlying causes and effects, emphasises the importance of reintegration and lays the groundwork for a more secure and inclusive society. ■
References
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/1418456/japan-number-juvenile-cases/
- https://www.nippon.com/en/japan-data/h01860/
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/1418559/japan-distribution-juvenile-cases-minors-detention-by-offense/
- https://www.unafei.or.jp/publications/pdf/RS_No111/No111_12_IP_Tsubura.pdf
- https://www.unodc.org/documents/justice-and-prison-reform/ReducingReoffending/MS/Japan_-_Input_on_reducing_reoffending.pdf
- https://www.msf.gov.sg/docs/default-source/ncpr/factsheet-on-youth-delinquency2fa97cee-baa3-401c-a986-71eb8871bb0b.pdf?sfvrsn=f3f45658_5
- https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/crime-and-justice/recorded-crime-offenders/latest-release
- https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/youth-justice/youth-justice-in-australia-annual-report-2022-23/contents/youth-justice-in-context
- https://factly.in/data-ncrb-data-indicates-that-crimes-committed-by-juveniles-down-30-between-2013-2022/
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/delhi/heart-of-darkness-major-crimes-by-minors-shoot-up/articleshow/105486240.cms
- https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/youth-justice-statistics-2022-to-2023/youth-justice-statistics-2022-to-2023-accessible-version
- https://ojjdp.ojp.gov/statistical-briefing-book/crime/faqs/qa05101#0-0
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/world/china/increase-in-juvenile-crimes-the-shocking-way-china-is-reacting-to-brutal-murders-of-little-girls/articleshow/111391229.cms
- https://academic.oup.com/edited-volume/41333/chapter/352357517
- https://www.police.gov.hk/ppp_en/09_statistics/csc.html
- https://www.info.gov.hk/gia/general/202408/10/P2024081000273.htm
- https://www.spp.gov.cn/spp/xwfbh/wsfbt/202306/t20230601_615967.shtml#2